- This simple story illustrates profound meaning in life.
- It teaches us to see life situation in different perspectives, angles.
- It motivates and inspires us to be a better person ourselves. :)
Monday, December 24, 2007
An Inspiring Story for all the students.........
Tuesday, December 18, 2007
SAMPLE PRACTICAL QUESTION PAPER
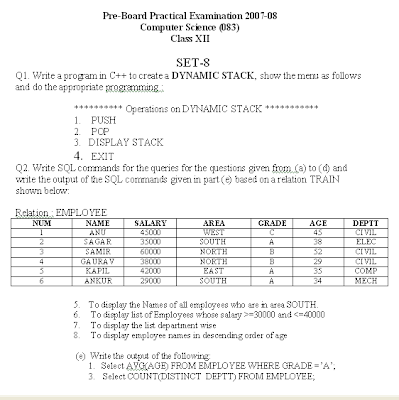
NOTE :
- Take the above Question paper just as a guideline for your Board Pr Exam.
- The Programming questions can be from any topic in your syllabus( Check the CBSE Syllabus given in previous post as it is taken straight from CBSE site http://www.cbse.nic.in/curric~1/xii06/compscie.pdf
- Students are supposed to submit program SOURCE CODE and OUTPUT Printouts
Computer Science (Code 083) (Practicals)
Class XII (Practicals)
(As per CBSE Syllabus)
Computer during the examination. Marks are allotted on the
basis of following:
Documentation/Indentation
Output presentation
the following topics
• Array of structure
• Stack using arrays and linked implementation
• Queue using arrays (circular) and linked implementation
• Binary File operations (Creation, Displaying, Searching and modification)
• Text File operations (Creation, Displaying and modification)
2. SQL Commands (05 Marks)
Five Query questions based on a particular Table/Relation to be tested
practically on Computer during the examination. The command along
with the result must be written in the answer sheet.
3. Project Work (05 Marks)
The project has to be developed in C++ language with Object Oriented
Technology and also should have use of Data files.
• Presentation on the computer
• Project report (Listing, Sample, Outputs, Documentation
• Viva
4. Practical File (05 Marks)
Must have minimum 20 programs from the following topics
5. Viva (05 Marks)
Based on C++ ,Project, SQL
Friday, December 14, 2007
Computer Science Project Report (C++)
- Certificate
- Acknowledgment
- Overview of C++
- Need for the Project/Synopses/Summary
- Requirements(hardware & Software) along with instructions regarding how to install the project and use it are to be given. It should be a sort of USER MANUAL
- Header Files (used in the Project along with the functions each file is supporting in the project.)
- Classes & Objects( Description of user defined classes and their purpose)
- Functions ( Description of user defined functions and their purpose)
- Source Code(listing of all the programs prepared as part of project. )
- Output (Dumps of all the output screens)
- Shortcomings
- Bibliography
- Index to be placed after Acknowledgment in the report but NOT to be mentioned in the index.
- Running project Source Code to be submitted in a CD along with relevant data files
- Project CD should be properly LABELED with
- Class : XII
- Section : A/B/E
- Year : 2007-08
- Class Roll No. :
- BOARD ROLL No. ( To be mentioned later)
- Project TITLE : Tutorial - Water Cycle (Example)
- Main Program name : (.CPP File name)
Wednesday, December 12, 2007
Mindmap : K-Map method of Minimization of Boolean Exp
Friday, December 7, 2007
Thursday, December 6, 2007
ASSIGNMENT (Boolean Algebra)
| Q1. | | Design NAND-to-NAND circuit for the following expressions |
| | a. | XYZ’ + X’Y’Z |
| | b. | A’B.(A’B’C’ + B’C) |
| | c. | A’B’C’ + A’B’C + A’BC + ABC’ + ABC |
| | d. | (X + Y’).Z |
| | e. | Y’ Z + Z X’ |
| | f. | (A+B) (B+D) |
| | g. | 3 input AND gate |
| | h. | 3 input OR gate |
| Q2. | | Design NOR-to-NOR circuit for the following expressions |
| | a. | X(Y’ + Z’) + XY’ |
| | b. | A’B.(A’B’C’ + B’C) |
| | c. | X.Y’ + Z |
| | d. | (X + Y) (Y + Z) (X+Z) |
| | e. | F(A,B,C) = (A+B’) (B+C) |
| | f. | F(X,Y,Z) = (X’+Y) (Y’+Z) |
| | g. | (A’+B’+C’) (A+B’+C’) (A+B+C’) |
| Q3. | | Obtain a simplified form of a Boolean Expression using Karnaugh Map |
| | a. | F(W,X,Y,Z)=S(2,3,6,10,11,14) |
| | b. | F(A,B,C,D)=S(0,1,3,45,6,7,9,10,11,13,15) |
| | c. | F(A,B,C,D)=P(0,1,3,45,6,7,9,10,11,13,15) |
| | d. | F(X,Y,Z)=P(3,4,5,6,7) |
| | e. | F(A,B,C,D)=S(0,1,2,5,6,8,9,10,13,15) |
| | f. | F(W,X,Y,Z)=S(2,3,6,10,11,14) Find expression in POS form |
| | g. | F(X,Y,Z)=S (3,4,5,6,7) |
| | h. | F(U,V,W,X)=S(7,9,10,11,12,13,14,15) |
| | i. | F(U,V,W,X)=P(0,2,3,7,8,10,11) |
| | j. | F(U,V,W,X)=P(3,4,5,6,7,9,11,12,13,14,15) Draw circuit diagrams for the simplified Boolean Expression |
Wednesday, December 5, 2007
Karnaugh Map Minimizer (Free Download)
Karnaugh Map Minimizer is free (GPL) software for minimizing boolean functions using the graphic method of Karnaugh maps. I am giving its link for downlods for educational purposes so double check the output if you intend to use it for any "real" work. I hope it helps you with the topic….
Minimization of Boolean Expresssions using Karnaugh Maps
Tuesday, December 4, 2007
Friday, November 30, 2007
Boolean Algebra (Basic Concepts)
- I have created another Mind Map On Boolean Algebra (Basic Concepts) as I am finding this tool very interesting, easy to work with and very useful in developing the topic. This tool is allowing me to discuss all the relevant points in depth and still maintaining the connectivity with the main topic. I would like to know your views about this tool.
- Click Here........... 'Boolean Algebra Mind Map'

SQL(Structured Query Language)
- I have created Mind Map on the topic 'SQL' Using Open Source Software FreeMind. I think my students will find it beneficial while preparing and revising this topic.
- To access the Mind Map Click Here.......

Monday, November 26, 2007
Database Concepts : Mind Map
- I have created this Mind Map to facilitate Organized learning and revision of the topic-'Database Concepts'.
- I have published my work for sharing on freemindshare.com
- The URL for this particular Mind Map is:

Sunday, November 25, 2007
Database Concepts
- –Concept of Domain
- –Tuple
- –Relation
- –Primary Key, Alternate Key, Candidate key
- –Selection
- –Projection
- –Union
- –Cartesian Product
Thursday, November 22, 2007
MCQ-12/02
Attempt this MCQ. I will post its answers after 2 days
Kulachi Hansraj Model School
Multiple Choice Questioner
(General Concepts, Header Files, File Handling)
Class XII
Time : 15 min. M.Marks : 30
1. When working with character arrays, always reserve enough array elements to hold the string AND its null-terminating character (\0).
[a] True [b] False
2. In C++, 14 % 4 =
[a] 1 [b] 2 [c] 3 [d] 4
3. Variables that are declared, but not initialized, contain
[a] blank spaces [b] zeros [c] "garbage" values [d] nothing - they are empty
4. Array indexing always starts with the number
[a] 0 [b] 1 [c] 2 [d] \0
5. A character variable may contain up to seven letters.
[a] True [b] False
6. All strings end with a null zero in memory.
[a] True [b] False
7. The name of a variable is known as its
[a] identifier [b] constant
[c] data type [d] base
8. In C++, the % refers to
[a] percentages [b] modulus operator
[c] division [d] data storage
9. A variable is given a value through
[a] osmosis [b] the cout statement
[c] the
10. Variable names may begin with a number.
[a] True [b] False
11. When a data type must contain decimal numbers, assign the type
[a] int [b] char [c] double [d] long int
12. Mathematicians and computers interpret the equal sign (=) in the same way.
[a] True [b] False
13. setprecision requires the header file
[a] stdlib.h [b] iomanip.h [c] console.h [d] conio.h
14. The following statement is valid. double price = 7,450.98;
[a] True [b] False
15. All variables must be declared before they can be used.
[a] True [b] False
16. Character literals always have a length of one.
[a] True [b] False
17. If char catname[15]; , which of the following is valid?
[a] catname[15] = "Millie"; [b] catname = "Millie";
[c] catname[ ] = "Millie"; [d] none are valid
18. Which type of data file is analogous to an audio cassette tape?
[a] random access file [b] sequential access file
[c] binary file [d] source code file
19. Which of the following header files is required for creating and reading data files?
[a] ofstream.h [b] fstream.h
[c] ifstream.h [d] console.h
20. If you create a file with the same name as an existing file, you will be prompted to rename your new file.
[a] True [b] False
21. In the code fout.open("scores.dat", ios::out);
[a] ios::out is the stream operation mode.
[b] fout is the header file reference.
[c] ios::out is the stream variable name..
[d] fout is the name of the file.
22. A text editor can be used to view, or create, a file.
[a] True [b] False
23. What header file contains C++ file I/O instructions?
[a] iostream.h [b] fstream.h
[c] infstream.h [d] outstream.h
24. ifstream fin; would be used when
[a] creating a file [b] reading a file
[c] appending a file [d] removing a file
25. eof( ) is the function used for
[a] asserting no errors in a file [b] appending data to a file
[c] counting the amount of data in a file [d] checking for end of file
26. If a file you are opening for appending does not exist, the operating system will detect the missing file and terminate the operation.
[a] True [b] False
27. It is possible to open several files for access at the same time.
[a] True [b] False
28. Which of the following is not a valid ofstream argument?
[a] ios::app [b] ios::trunc
[c] ios::noreplace [d] ios::create
29. What does ios::ate mean as an argument to ofstream?
[a] Open file, but do not create. [b]Open file, create.
[c] Open file for read access only.[d]Open file, set the position to the end.
30. How would you output to an open file named a_file?
[a] a_file.out("Output"); [b] a_file="Output";
[c] a_file<<"Output"; [d]a_file.printf("Output");
Wednesday, November 21, 2007
Linked Queue : C++ Code
Struct NODE
{
int Data;
NODE *Next;
};
class Queue
{
NODE *Rear,*Front;
public:
Queue(){Rear=NULL;Front=NULL;}
Void Qinsert();
Void Qdelete();
Void Qdisplay();
~Queue();
};
_______________________________________________________________
void Queue::Qinsert()
{
NODE *Temp;
Temp=new NODE;
Cout<<”Data:”;
Cin>>Temp->Data;
Temp->Next=NULL;
If (Rear==NULL)
{
Rear=Temp;
Front=Temp;
}
else
{
Rear->Next=Temp;
Rear=Temp;
}
}
_______________________________________________________________
void Queue::Qdelete()
{
if (Front!=NULL)
{
NODE *Temp=Front;
Cout<
Front=Front->Next;
Delete Temp;
If (Front==NULL) Rear=NULL;
else
cout<<”Queue Empty..”;
}
_______________________________________________________________
void Queue::Qdisplay()
{
NODE *Temp=Front;
While(Temp!=NULL)
{
cout<
Temp=Temp->Next;
}
_______________________________________________________________
void Queue::~Queue()//Destructer Function
{
while (Front!=NULL)
{
NODE *Temp=Front;
Front=Front->Next;
delete Temp;
}
}
_______________________________________________________________
void main()
{
Queue QU; char Ch;
do
{
}while (Ch!=’Q’);
}
_______________________________________________________________
Tuesday, November 20, 2007
Linked Stack : c++ code
{
int Data;
NODE *link;
};
class LStack
{
NODE *Top;
Public:
LStack(){Top=NULL;}
void Push();
void Pop();
void show_stack();
~LStack();
};
void LStack::Push()
{
NODE * ptr;
ptr=new NODE;
cout<<”Data:”;
cin>>ptr->Data;
ptr->link=Top;
Top=ptr;
}
void LStack::Pop()
{
if (Top!=NULL)
{
NODE *Temp=Top;
Cout<
Top=Top->link;
delete Temp;
}
else
cout<<”Stack Empty..”;
}
void LStack::show_stack()
{
NODE *Temp=Top;
while(Temp!=NULL)
{
cout<
Temp=Temp->link;
}
}
void LStack::~LStack() //Destructer Function
{
while (Top!=NULL)
{
NODE *Temp=Top;
Top=Top->Next;
delete Temp;
}
}
void main()
{
Stack ST; char Ch;
do
{
cout<<”P/O/D/Q”;cin>>Ch;
switch (Ch)
{
case ’P’:ST.Push();break;
case ’O’:ST.Pop();break;
case ’D’:ST.show_stack();
}
}
while (Ch!=’Q’);
} // Destructor function will be called
// automatically when the scope of the
// object gets over








